
Understanding total hip replacement
Serious hip joint conditions can cause pain, reduced range of motion, and decreased quality of life.

Those conditions include Osteoarthritis, Osteonecrosis, Rheumatoid Arthritis, Traumatic Arthritis or Traumatic Injury. The key is finding a way to restore your mobility, provide pain relief, and allow you to get back to your daily activities. That’s why your physician may recommend a total hip replacement with a hip implant system from MicroPort Orthopedics, a company with an established track record of developing new and better ways to address hip replacement. We know that the prospect of hip replacement surgery is an important choice for you. We’ve provided this brochure as a resource to enable you to learn more about how our implants can provide a solution to help you get back to the life that you love.
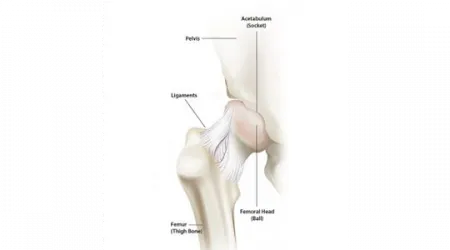
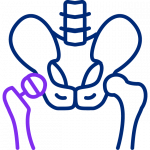
Hip anatomy
The hip is the most flexible and free-moving joint in the body. Each of your hips move backwards, forwards, side-to-side and even twist countless times during a normal day. This is possible because of the ball-and-socket joint structure where the thigh bone (femur) has a ball at the top (femoral head) that fits into the socket (acetabulum). The surface of the ball and socket is covered by smooth and nearly friction-free material called cartilage, which protects and cushions the bones and allows them to move more easily.
The joint is also lubricated with a small amount of fluid to minimize wear and pain during your lifetime. It is held together with ligaments—straps of tough tissue, which prevent the joint from dislocating. A fully functioning hip joint also depends on the coordination of many interrelated parts from bones to muscles, tendons, ligaments and nerves.
Why does my hip hurt?
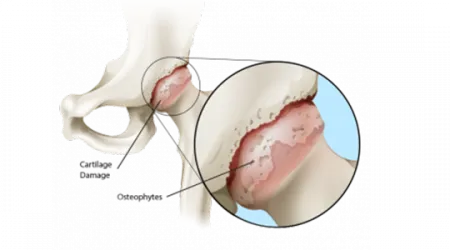
There are a variety of conditions that can lead to hip joint deterioration, resulting in pain, reduced range of motion and decreased quality of life. When cartilage in the hip joint is damaged or worn down by disease, your hip bones literally begin to rub together, resulting in friction, pain and even bone deterioration. Worn cartilage is typically associated with arthritis, or osteoarthritis, the most common type of arthritis leading to hip replacement. Osteoarthritis is just one of the many forms of arthritis, which can result in individuals experiencing pain and limited activity level. Other forms of arthritis include: Rheumatoid Arthritis, Osteonecrosis and Traumatic Arthritis.

WHAT IS OSTEOARTHRITIS?
The joints in our bodies are cushioned by cartilage. As we age, normal wear and tear (or degeneration) of the cartilage takes place in most joints. With osteoarthritis, the cartilage cushioning the bone surfaces wears away, causing the bones to rub against each other, creating pain.

WHAT IS OSTEONECROSIS?
Osteonecrosis or avascular necrosis occurs when an area of the bone loses its blood supply. This causes the bone to die and subsequently break down. Osteonecrosis of the hip joint accounts for over 90 percent of all osteonecrosis cases. Primarily seen in people ages 20 to 40, it is predominantly found in men.

WHAT IS RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS (RA)?
Rheumatoid arthritis occurs when the body’s own immune system attacks the synovial lining of the joints, just as it would foreign bacteria. Synovial fluid is a clear, smooth, oil-like lubricating liquid that makes it easier for the joints to move. With RA, there is more friction in every movement of the hip and this causes pain.

WHAT IS TRAUMATIC ARTHRITIS?
Traumatic arthritis results when the joint, or the ligaments surrounding it, are damaged by fracture, dislocation, or other accident-related injury. All arthritic conditions result in stiffness, swelling, and the loss of motion. It becomes difficult to put pressure on the hip, and the joint becomes increasingly tender and swollen. As time passes, arthritis of the hip can significantly affect your ability to walk.

WHAT IS NON-ARTHRITIC TRAUMA?
In addition to arthritis, hip replacement surgery may be recommended for individuals whose hip has been injured as the result of trauma. This could be a hip fracture or dislocation caused by a fall or other injury to the hip.
The conditions that cause hip degeneration and pain are routinely not reversible. Indeed, they typically just get worse over time. For these reasons, your doctor may recommend a total hip replacement surgery, or hip arthroplasty, to treat your condition and ideally restore your mobility and quality of life.
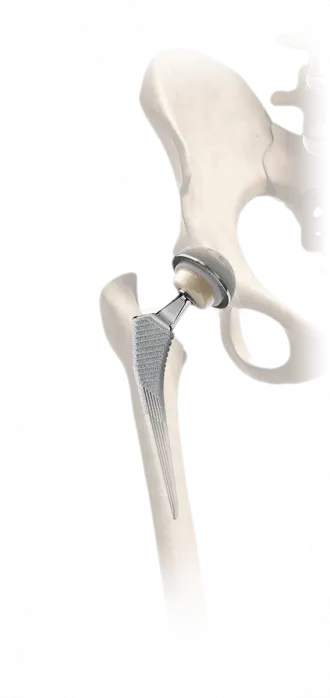
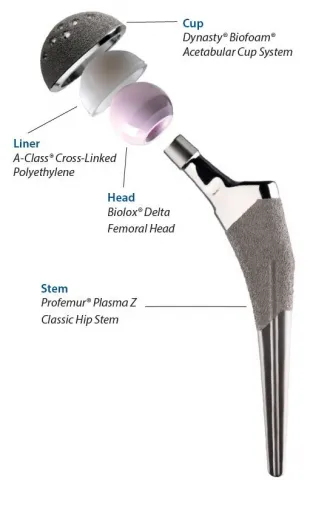
Total hip replacement surgery is performed by means of an open incision. A typical operation may take one to several hours. The diseased ball end of the thigh bone (the femur) is removed so that the socket (acetabulum) can be seen. The bony socket is fashioned to contain a new metal socket, called a cup.
The femur is subsequently prepared for the stem. Once the stem is placed in the femur, a smooth ball is attached. The ball is then placed in the socket and the surgery is finished.
Your new hip is designed to mimic the feel and function of your natural hip to the fullest extent possible. While results vary, the goal at MicroPort is simple. We want to help you regain normal mobility and ultimately forget that a hip replacement even took place.
Through innovation in implant technology and less invasive surgical techniques, MicroPort is continually working to create products that can dramatically improve the lives of patients

PRECAUTIONS & DISCLAIMERS
Every patient is different, and individual results will vary. There are risks and recovery times associated with surgery. Consult your doctor to determine if joint replacement surgery is right for you.
Individual results and activity levels after surgery vary and depend on many factors including age, weight and prior activity level. There are risks and recovery times associated with surgery and there are certain individuals who should not undergo surgery. Please click here to read about risks associated with surgery. Only a physician can tell you if this product and associated procedure are right for you and your unique circumstances. Please consult with a physician for complete information regarding benefits, risks and possible outcomes.