Firehawk™ Stent Family
Next-Generation Target-Eluting Stent (TES) Platform
The Firehawk™ family of stents is among the few drug-eluting stents (DES) supported by both 1‑ and 3‑month DAPT regimens. The clinical evidence includes reduced DAPT strategies - 1‑ or 3‑month DAPT (aspirin + P2Y12 inhibitor), followed by either aspirin or P2Y12 inhibitor monotherapy - covering patients at high bleeding risk (HBR) and demonstrating robust outcomes in clinical practice.
Short DAPT: Stent Type Comparison
TARGET DAPT Study and TARGET-FIRST Study: Firehawk™ Stent demonstrated very low rates of stent thrombosis (ST) at 12 months:
Firehawk™ Stent is recognized for its low ST rate and demonstrated significantly strong anti-thrombotic performance compared with other DES. This advantage is evident even with short DAPT durations. For example, Firehawk™ Stent with 3-month DAPT had an ST rate of 0.3%, compared with 0.2% at 12 months with standard DAPT.
Shortening dual-antiplatelet therapy (DAPT) duration from 1-year to 1-month after complete revascularization with Firehawk™ stents in selected low-risk acute myocardial infarction (AMI) patients showed non-inferior ischemic outcomes and superior reduction in clinically relevant bleeding.
Primary endpoint: Net Adverse Clinical and Cerebral Events (NACCE) defined as a composite of all cause death, non-fatal myocardial infarction, definite/probable stent thrombosis, stroke, or Bleeding Academic Research Consortium (BARC) type 3 or 5 bleeding at 11 months post randomization (12 months post index procedure). Rates of the primary end point were comparable between both groups (2.1% vs 2.2%; p for non-inferiority = 0.021).
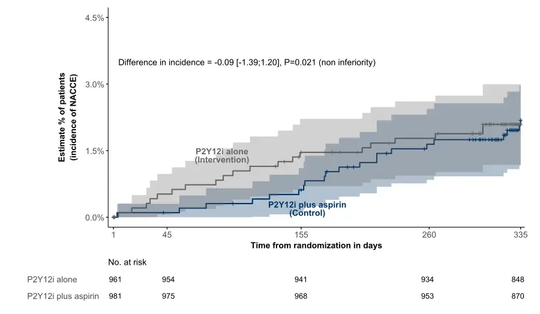
Main secondary endpoint (powered): BARC type 2, 3 or 5 bleeding events at 11 months post randomization. Firehawk™ Stent showed significant lower bleeding events rate with 1-month DAPT regimen comparing to 12-month with standard DAPT(2.6% vs. 5.6%;p=0.002).
1.Ge, J., et al. EuroPCR 2024, TARGET DAPT Trial
2. Yang H, et al. BMJ Open 2019;9:e033774
3. Tarantini G, et al. EuroIntervention 2023;19:240-247.
4. TARANTINI G, et al. ESC Congress 2025, TARGET FIRST Trial
The Firehawk™ and Firehawk Liberty™ are indicated for improving coronary luminal diameter in patients with symptomatic heart disease due to de novo native coronary artery lesions length ≤ 60 mm with reference vessel diameters of ≥ 2.25 to ≤ 4.0 mm.
The Firehawk™ and Firehawk Liberty™ are contraindicated for use in patients:
• Who cannot receive antiplatelet and/or anti-coagulant therapy
• With lesions that prevent complete angioplasty balloon inflation or proper placement of the stent or stent delivery system
• With hypersensitivity or contraindication to rapamycin or similar drugs or any other analogue or derivative, cobalt, chromium, nickel, tungsten, or PLA
• Ensure that the inner package sterile barrier has not been opened or damaged prior to use.
• Judicious patient selection is necessary since the use of the device carries the associated risks of thrombosis, vascular complications, and/or bleeding events.
• This product should not be used in patients who are not likely to comply with the recommended antiplatelet therapy.
General Precautions
• Stent implantation should only be performed by physicians who have received appropriate training.
• Stent placement should be performed at hospitals where emergency coronary artery bypass graft surgery is accessible.
• Subsequent restenosis may require repeat dilatation of the arterial segment containing the stent. Long-term outcomes following repeat dilatation of the stent are presently unknown.
• Risks and benefits should be considered in patients with severe contrast agent allergies.
• Do not expose or wipe the product with organic solvents such as alcohol or detergents.
• Care should be taken to control the guiding catheter tip during stent delivery, deployment, and delivery system withdrawal. Before withdrawing the stent delivery system, visually confirm complete balloon deflation by fluoroscopy to avoid guiding catheter advancement into the vessel and subsequent arterial damage.
• Compared to use within the specified Indications for Use, the use of DES in patients and lesions outside of the labeled indications may have an increased risk of adverse events, including stent thrombosis, stent embolization, MI, or death.
• It is very important that the patient comply with post-procedural antiplatelet therapy recommendations. It should be adapted depending on patient profile, clinical indication and intervention characteristics, and in accordance with ESC and ACC/AHA/SCAI guidelines.
• Early discontinuation of prescribed antiplatelet medications could result in a higher risk of stent thrombosis, MI, or death. The risks and benefits of the procedure should be weighed against the possible risks associated with early discontinuation of antiplatelet therapy. Patients who require early discontinuation of antiplatelet therapy should be monitored carefully for cardiac events.
• Orally administered sirolimus combined with cyclosporine is associated with increased serum cholesterol and triglycerides levels.
• When used with cyclosporine medication, The sirolimus mean AUC and mean Cmax may be affected
Adverse events may be associated with the implantation of a coronary stent in coronary arteries, but are not limited to the following:
• Allergic reaction to anti-coagulant and/or antiplatelet therapy, contrast medium, or stent materials
• Arrhythmias
• Arteriovenous fistula
• Bleeding
• Cardiac tamponade
• Coronary aneurysm
• Death
• Dissection
• Drug interactions with antiplatelet/anticoagulant/contrast medium
• Emboli, distal (tissue, air, or thrombic emboli)
• Embolization, stent
• Emergency CABG
• Failure to deliver the stent to the intended site
• Fever
• Heart failure
• Hemorrhage
• Hypotension/Hypertension
• Infection, local or systemic
• Myocardial infarction
• Pain, at the access site
• Pseudoaneurysm, femoral
• Restenosis of stented segment
• Stent embolization or migration
• Stent fracture
• Stent thrombosis/occlusion
• Target lesion revascularization
• Target vessels of non-target lesion revascularization
• Total occlusion of coronary artery
• Vessel trauma requiring surgical repair or reintervention
Potential adverse events not captured above, that may be unique to the rapamycin drug coating
• Abnormal liver function tests
• Allergic/immunologic reaction to drug (rapamycin or structurally-related compounds) or the polymer stent coating or its individual components (see Section 1 Product Description)
• Anemia
• Arthralgias
• Diarrhea
• Hypercholesterolemia
• Hypersensitivity, including anaphylactic/anaphylactoid type reactions
• Hypertriglyceridemia
• Hypokalemia
• Infections
• Interstitial lung disease
• Myocardial infarction
• Myocardial ischemia
• Occlusion
• Prolonged angina
• Pseudoaneurysm
• Hematologic dyscrasia (including leukopenia, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia)
• Renal failure
• Restenosis of stented segment (greater than 50% obstruction)
• Stroke
• Vessel spasm
• Vessel perforation